Head Injury Criterion (HIC)
Overview
An industry standard, the Head Injury Criterion (HIC) is a measure of the maximum weighted integral of resultant translational acceleration over any 15 ms or 36 ms duration of an impact event [1]. It is based on the integral of head acceleration measured at the Head CG. Historically, HIC is based on the Wayne State Tolerance Curve (WSTC) and is calculated according to Equation 1.
The Skull Fracture Correlate (SFC) was based on Post Mortem Human Subject Tests (PMHS) performed in Vorst et al. (2003). SFC is calculated by averaging the acceleration over the HIC time interval [2]. Both HIC and SFC are noted to have limitations due to only using linear acceleration and not taking into account a rotational compenent.
Required Signals
- Head Linear Acceleration at Head CG (, and )
Calculation
- Each head acceleration is filtered at CFC = 1000.
- Calculate the resultant head acceleration
- Convert the acceleration to G's ()
- HIC, SFC and SFC Probability are calculated using Equation 1, 2, and 3, respectively
where t1 and t2 are any two arbitrary times during the head CG resultant acceleration pulse a(t)
Examples
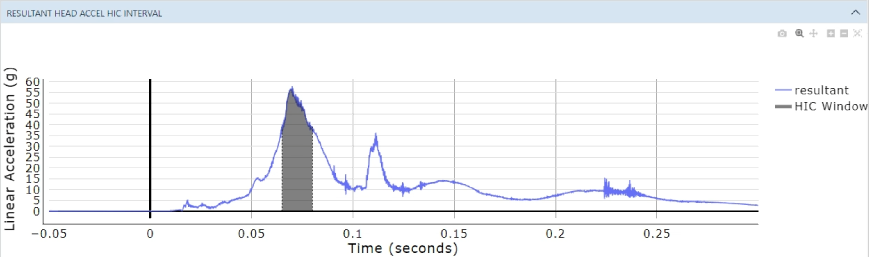
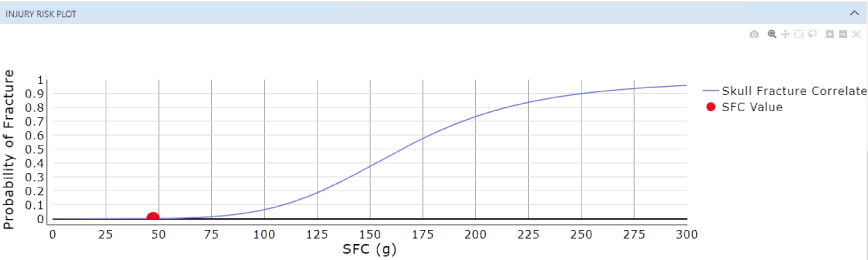
References
[1] Hertz (1993) A Note on the Head Injury Criteria (HIC) as a Predictor of the Risk of Skull Fracture. 37th Annual Proceedings of the Association for the Advancement of Automotive Medicine.
[2] Vander Vorst, Michael et al. “Statistically and biomechanically based criterion for impact-induced skull fracture.” Annual proceedings. Association for the Advancement of Automotive Medicine vol. 47 (2003): 363-81.